Recently I was listening to Elena Aguilar on the excellent podcast, Cult of Pedagogy from Jennifer Gonzalez, How to Build Psychological Safety in Professional Development. Aguilar explained how SEL is connected to adult learning by creating a safe and caring environment.
The approach toward students is similar. Without a safe and caring environment, students won’t take risks and learning is often shallow. To develop deep thinkers and problem solvers, we need students with strong SEL skills. Here’s seven tips (with practical resources to support each one) to seamlessly integrate SEL into your daily classroom routines.
1. Check ins
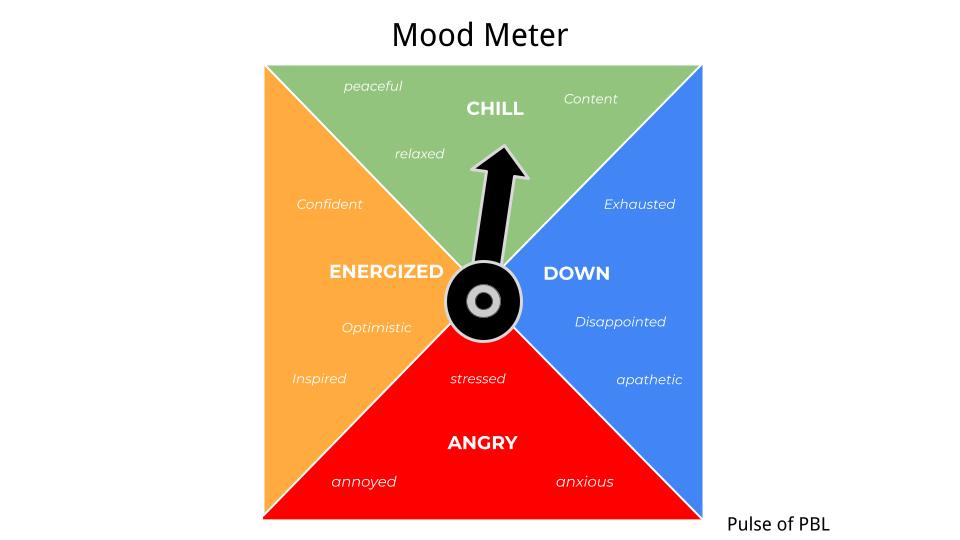
Self-Awareness begins with students recognizing their emotional state. Start off each day or class with a quick check in using a mood meter like the one above or try some fun How do you feel on a scale of… images. This sets a caring tone as students arrive and only needs to take a few minutes of class time.
My students enjoy making their own “scales” based on their hobbies, pets, or interests. It personalizes and humanizes the classroom. I have my middle school students check in with a neighbor student, but am always watching body language for students who seem “off” from their normal selves. It is important to follow up in private with students who self-report that they are not ok that day.
2. Reflection

Reflection is a part of all five of the SEL competencies. It cements learning into the brain’s long term memory. Reflection builds students’ self-awareness when they realize their growth points and struggles in the classroom. It is also tends to be an easy part of class to skip or forget which is why I include it in my lesson plans.
Throughout the day take time to reflect on content, processes, and SEL skills. You can use protocols such as turn and talk or exit tickets to quickly think about how each student or the whole class met an SEL goal. Try downloading and using one of the SEL Learning Targets above. Reflection does not need to be long; it needs to be a consistent practice.
3. Written and Verbal Communication
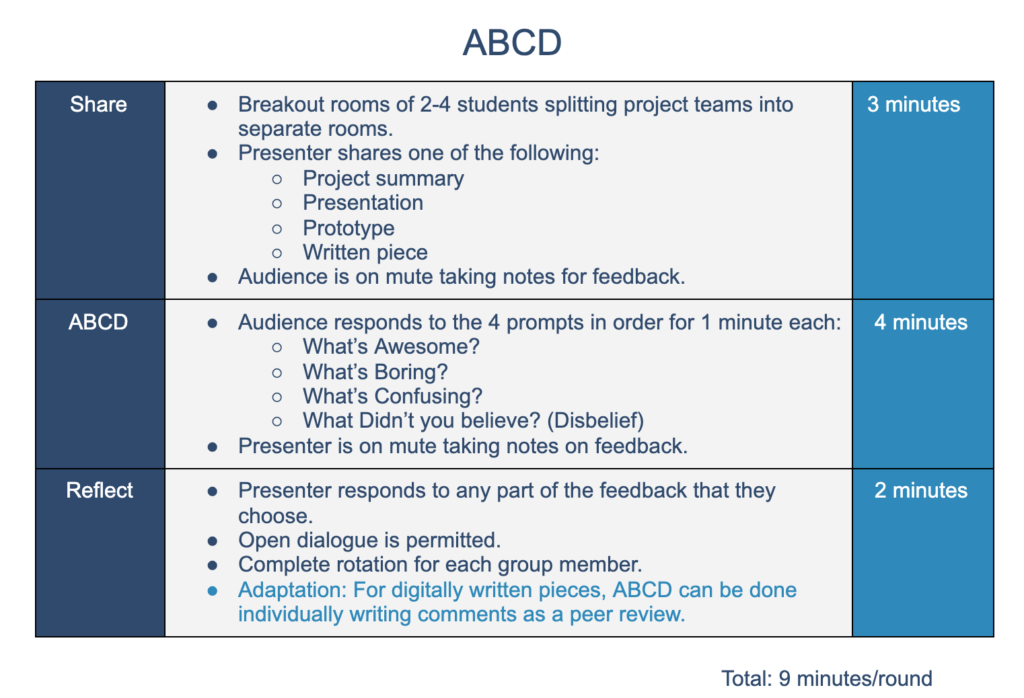
Communication is a key part of both Relationship Skills and academic learning. We want students to not only be able to articulate their learning in written and verbal ways, but to use communication skills to successfully collaborate with each other and the community.
An advanced level of communication is when students are able to give and receive feedback. Students do not naturally have these skills, but must be explicitly taught them. Using student discussion and feedback protocols helps them to navigate a variety of opinions in respectful ways. Through practice, students will become experts at sharing their ideas and improving each others’ work.
4. Collaboration
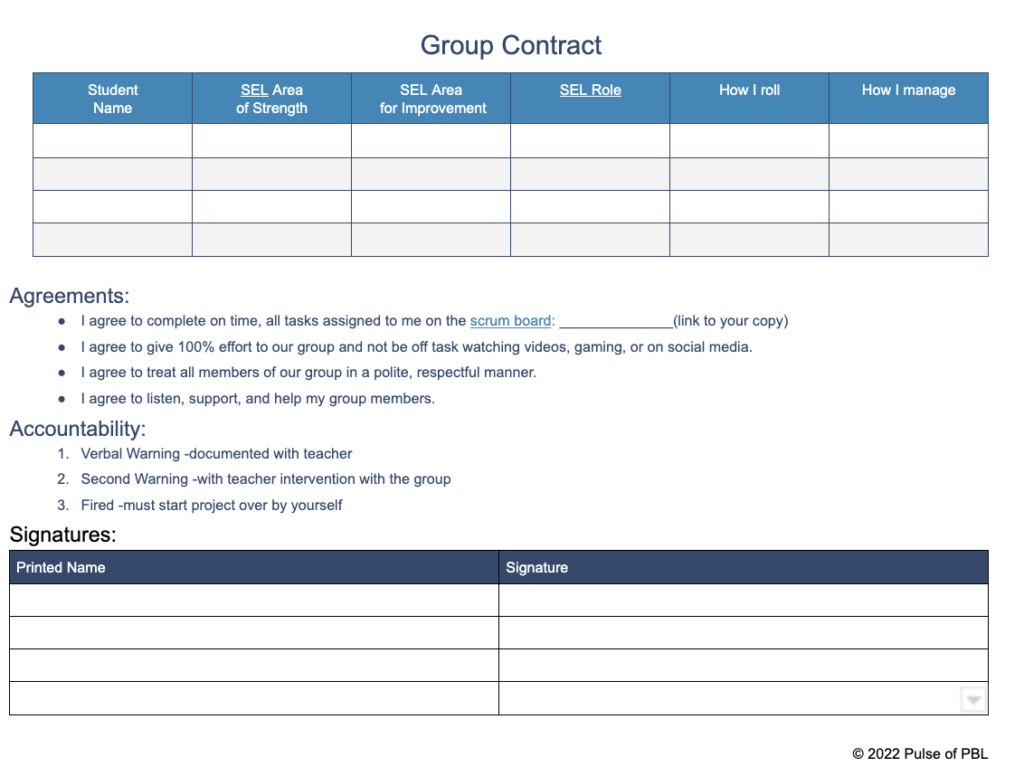
Another prominent Relationship Skill is collaboration. Help students effectively work together by creating group contracts at the beginning of the process before any potential conflict begins. Students can list their SEL strengths and an SEL Learning target that they want to improve on.
SEL group roles ensure that students are focused, not only on completing their work with the team, but on growing their collaboration skills. Including them in the contract, ensures that students discuss their SEL strengths and goals upfront so that they can support one another throughout the process.
5. Organization
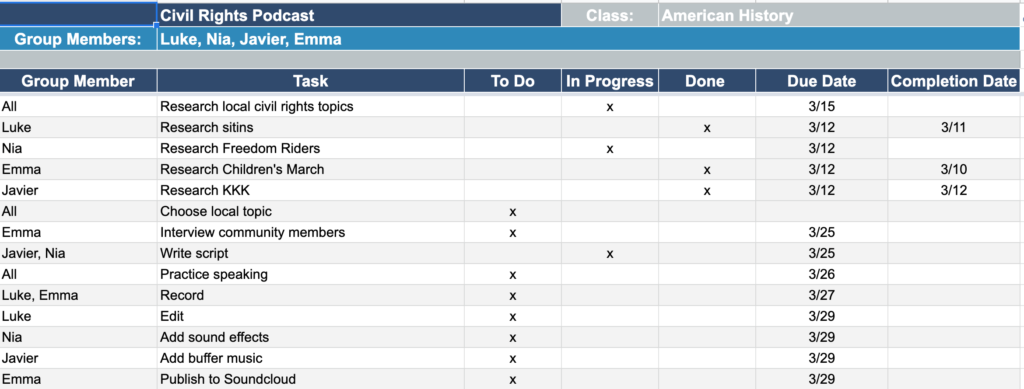
Self-Management means students can organize their project themselves. Group contracts are a great starting point, but many students struggle to organize the 3 T’s: their task, time, and team. Scrum boards are a project management tool used in the business world that can help students effectively complete quality work on time.
Students list the different parts of the project and then assign members and deadlines to each one. Start each class with students checking their scrum board and creating daily goals. The teacher can conference with groups during work time to discuss their gains while looking at their scrum board. As students complete tasks they move them into the done column so that they can see their progress.
6. Problem-Solving
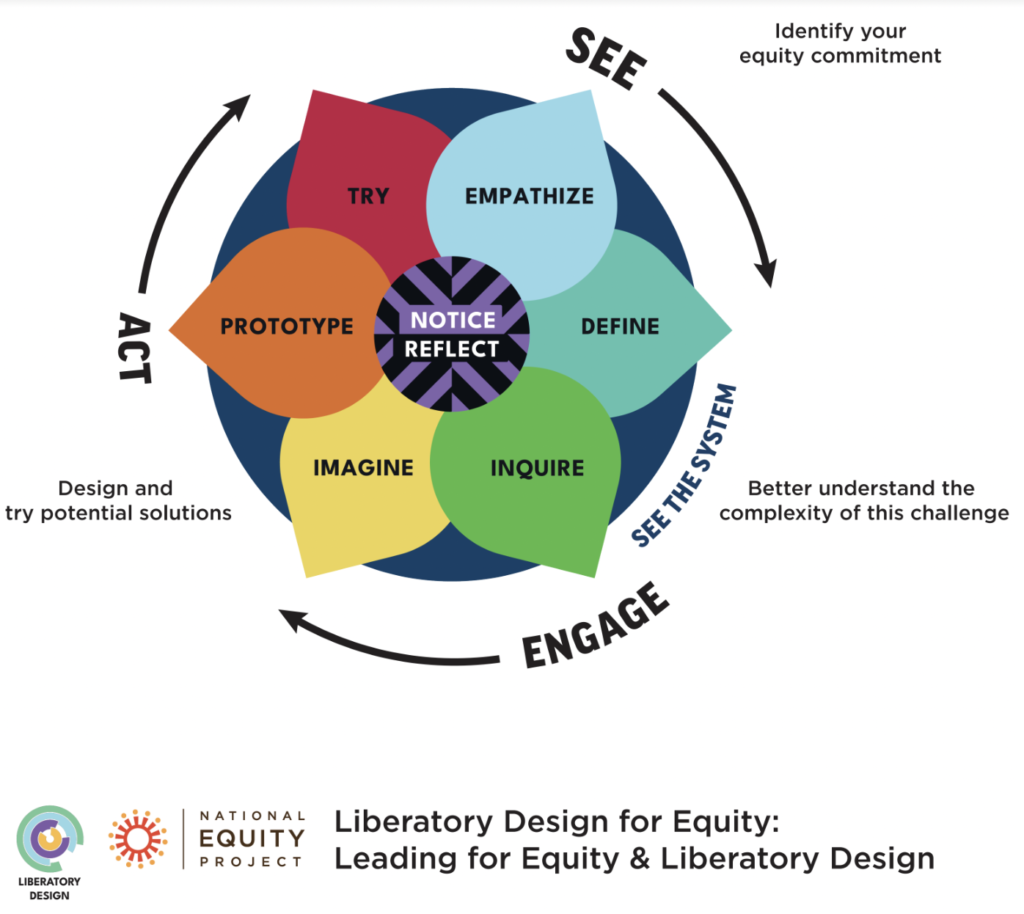
Responsible Decision-Making requires students to solve problems at a personal level and in the world in which they live. Design thinking processes (such as my favorite above) structure student inquiry so that they can successfully explore local and global issues. Notice that empathy (Social Awareness) and reflection are key ingredients of the cycle.
As students research both the source and possible solutions to problems, they should consider multiple viewpoints. Design Thinking pushes academic content into an authentic context increasing engagement and purpose. When students present their findings, they circle back to the SEL skills of persuasive communication and collaboration.
7. PBL
All of the tips above can be combined in Project Based Learning. The opportunities to practice all of the SEL competencies are naturally part of the daily PBL classroom routines. It is the ideal framework to teach academic content and SEL skills simultaneously. We don’t need to sacrifice deeper learning for SEL. Rather SEL promotes deeper learning.
We know that effective SEL instruction must be embedded throughout the day and modeled by the teacher. In PBL, students work collaboratively to solve problems. They communicate with each other and community partners. The authentic deeper learning grows student confidence, creating leaders in the community.
Learn with me!
Are you interested in professional development for your school on how to integrate SEL or implement PBL? I would love to have a conversation on how I can help. I am now scheduling summer workshops and book studies. Check out my workshop page or drop me an email at mikejkaechele@gmail.com. I would love to chat and co-plan meaningful PD for the educators at your school.
Would you like to explore more deeply how to integrate SEL into daily classroom activities? Check out my book below for tons of practical ways that can be immediately implemented in any classroom.
Pulse of PBL